Introduction to Computer
In the modern era, computers are an essential part of our everyday existence. That means computers are present in almost every field, making our day-to-day tasks easier and faster. Nowadays, computers can be seen in banks, shops, schools, hospitals, railways, and many more places, including our home. As they are such an essential part of our lives, we must know about the basic computer introduction. Let us start with defining the computer first:
What is a Computer?
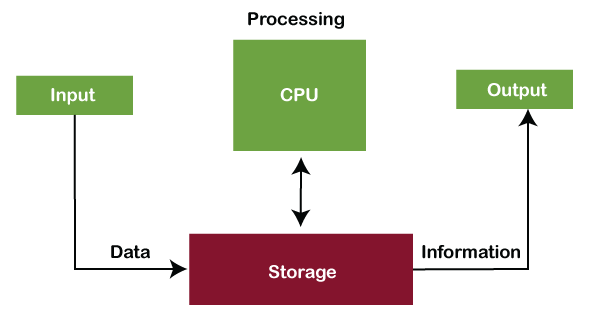
The straightforward meaning of a computer is a machine that can calculate. However, modern computers are not just a calculating device anymore. They can perform a variety of tasks. In simple terms, a computer is a programmable electronic machine used to store, retrieve, and process data.
According to the definition, "A computer is a programmable electronic device that takes data, perform instructed arithmetic and logical operations, and gives the output."
Whatever is given to the computer as input is called 'data', while the output received after processing is called 'information'.
A Brief History of Computer
The term 'Computer' was first introduced in 1640 and referred to as 'one who calculates'. It was derived from the Latin word 'computare', which meant 'to calculate'. In 1897, it was known as the 'calculating machine'. Later in 1945, the term 'computer' was introduced as 'programmable digital electronic computer, which is now called a 'computer'.
When the computers were introduced, they were large and could fill an entire room. Some computers were operated using large-sized vacuum tubes. In 1833, Charles Babbage (known as the father of the computer) invented an early calculator, which was named as the 'difference engine'. Later in 1837, he introduced the first mechanical, general-purpose computer 'Analytical Engine'. Over time, computers became powerful in performance and small in size.
Generations of Computer
There are five generations of the computer, which can be classified as below:
First Generation (1946 - 1959): During the first generation, computers were based on electronic valves (Vacuum Tubes). Some popular computers of first-generation are ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, etc.
Second Generation (1959 - 1965): During the second generation, computers were based on Transistors. Some popular computers of second-generation are IBM 1400, IBM 1620, IBM 7000 series, etc.
Third Generation (1965 - 1971): During the third generation, computers were based on Integrated Circuits (ICs). Some popular computers of the third generation are IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP, etc.
Fourth Generation (1971 - 1980): During the fourth generation, computers were based on very large scale integrated (VLSI) circuits. Some popular computers of fourth-generation are STAR 1000, CRAY-1, CRAY-X-MP, DEC 10, etc.
Fifth Generation (1980 - Present): The fifth generation is still ongoing. The computers are based on multiple technologies, such as ultra large scale integration (ULSI), artificial intelligence (AI), and parallel processing hardware. The fifth generation of computers includes Desktop, Laptop, NoteBook, etc.
Computer Software and Hardware
Software
Computer software is a group of instructions or programs that instructs the computer system to work accordingly. There are mainly two types of software:
System Software: System software help establish communication between hardware components so that the user can interact with the computer. These types of software are necessary for the computer to operate correctly. They provide an interface to run additional third party programs or utility tools. Operating systems, drivers, utility software, and firmware are typical examples of the system software.
Application Software: Application software is designed to help users to perform specific tasks, such as online surfing, setting the alarm, listening to music, playing videos, photo designing, editing, etc. This type of software mostly runs in the frontend and allows end-users to work on. Web browsers, Photoshop software, multimedia software and word processors are the example of the application software.
Hardware
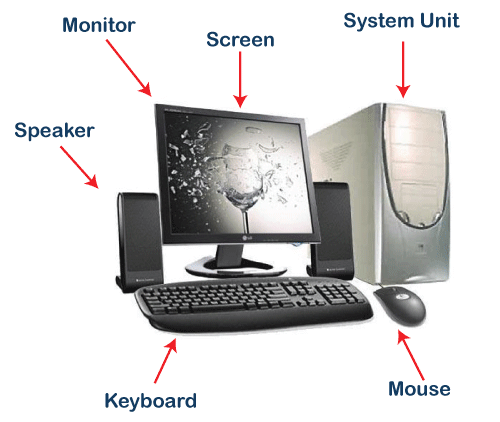
The physical parts attached to a computer that form a whole computer are called hardware or hardware components. There can be different types of hardware, depending on the structure. Some most common hardware are mouse, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc. These are the parts that can be seen and touched by humans.
Basic Parts of Computer
The essential components of the computer can be defined as follows:
Input Unit: Input Units or devices are used to input the data or instructions into the computers. Some most common input devices are mouse and keyword.
Output Unit: Output Units or devices are used to provide output to the user in the desired format. The most popular examples of output devices are the monitor and the printer.
Control Unit: As its name states, this unit is primarily used to control all the computer functions and functionalities. All the components or devices attached to a computer interact with each other through the control unit. In short, the control unit is referred to as 'CU'.
Arithmetic Logic Unit: The arithmetic logic unit helps perform all the computer system's arithmetic and logical operations. In short, the arithmetic logic unit is referred to as 'ALU'.
Memory: Memory is used to store all the input data, instructions, and output data. Memory usually has two types: Primary Memory and Secondary Memory. The memory found inside the CPU is called the primary memory, whereas the memory that is not the integral part of the CPU is called secondary memory.




No comments:
Post a Comment